1、 Electrophoretic treatment
Electrophoresis is an electrophoretic coating between the anode and cathode of a coating. Under voltage, charged coating ions move to the cathode and form an alkaline action generated by the surface of the cathode, depositing on the surface of the workpiece. Aluminum type electrophoresis refers to the process of placing extruded aluminum alloy in an electrophoresis tank and forming a dense resin film after flowing. Electrophoretic aluminum profiles are very bright and have a mirror effect, which also improves corrosion resistance.
Electrophoretic component pre-treatment (degreasing film), electrolysis (decomposition), electrophoresis (swimming), electrodeposition (precipitation), electroosmosis (dehydration)
2、 Anodizing
Anodized aluminum profiles refer to the process of forming an oxide film on aluminum products (anodes) under the action of specific methods of corresponding electrolytes and aluminum and its alloys. However, the oxide film formed by the surface of anodized aluminum oxide is different from general oxide films, and anodized aluminum oxide can be stained with electrolytes. In order to overcome the defects and wear resistance of aluminum alloys, expand their application range, and extend their service life, surface treatment technology has become an essential part of the use of aluminum alloys, and anodizing technology is currently the most widely used technology.
Degreasing, Chemical Polishing, Acid Corrosion, Stripping of Black Film, Anodizing, Coloring, Sealing, and Drying.
The difference between anodizing and electrophoresis: First, anodizing is followed by coloring, while electrophoresis directly colors.
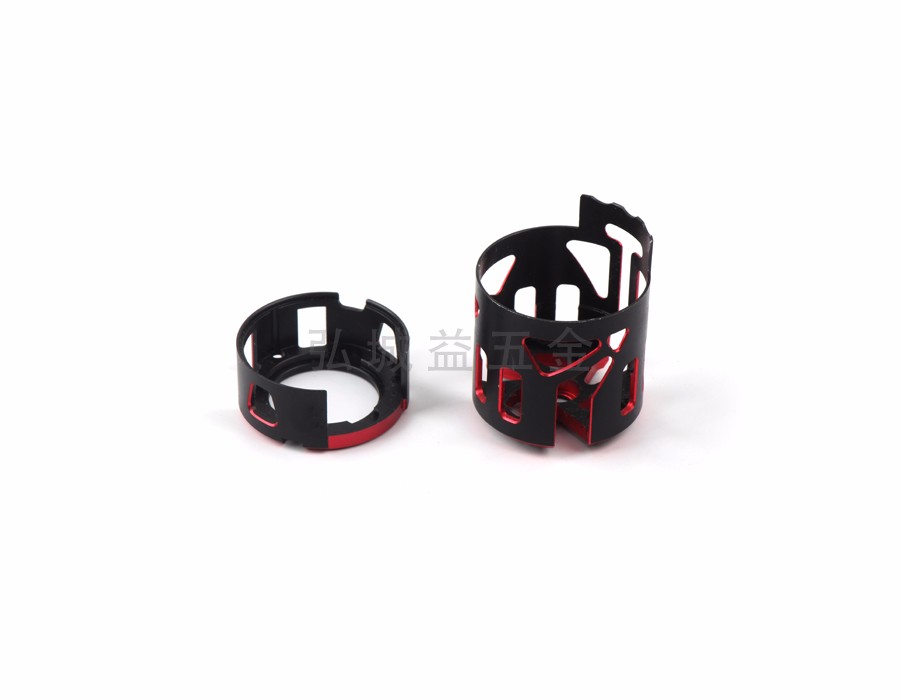

After machining product parts, some require surface treatment and oxidation. Anodizing can be divided into hard oxidation and ordinary oxidation. The thickness of hard oxidation is thicker than that of ordinary oxidation, and the hardness is higher than that of ordinary oxygen.
3、 Electrostatic spraying
Spray the powder coating onto the surface of the workpiece using an electrostatic powder device. Under the electrostatic device, the powder is evenly adsorbed onto the surface of the workpiece, forming a powdery coating. The powder coating has the effect of high-temperature baking flow curing and becoming each final coating. The mechanical strength, adhesion, corrosion resistance, and aging resistance of the spraying effect far exceed previous painting processes