Alloy steels with a chromium content greater than 12%or nickel content greater than 8%are called stainless steel.
This steel has a certain corrosion resistance in the atmospheric or corrosive medium, and has a high strength at a higher temperature (> 450 ° C). Steel with a chromium content of 16%to 18%is called acid -resistant steel or acid -resistant stainless steel, commonly known as stainless steel.
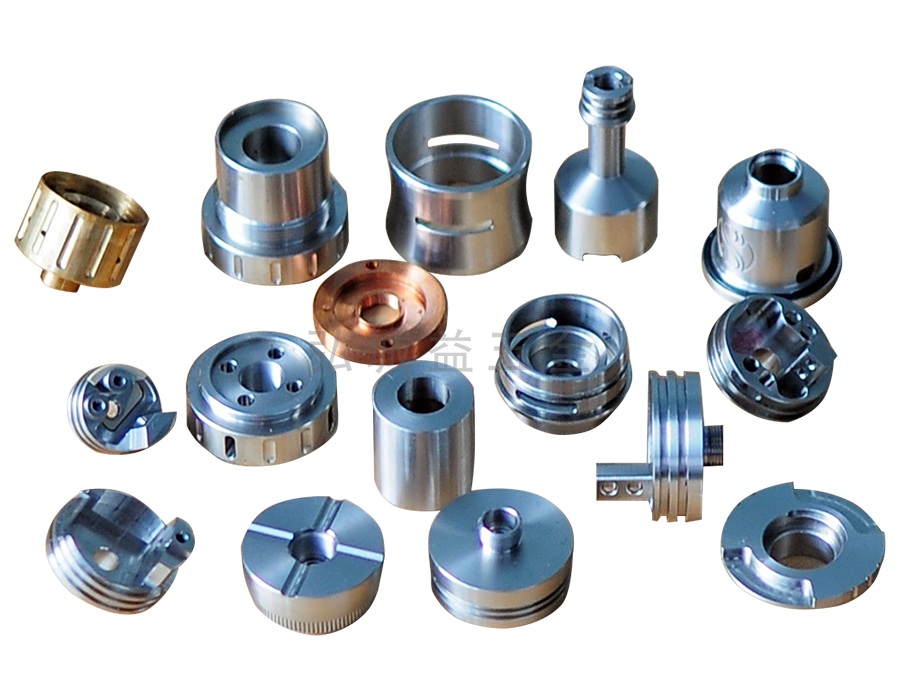
Due to the above characteristics of stainless steel, it is increasingly widely used in industrial departments such as aviation, aerospace, chemical, oil, construction, food and other industrial departments and daily life.
The following difficulties will be encountered during stainless steel processing:
Severe processing of processing: stainless steel plasticity, plastic deformation timing characteristics, and large reinforcement coefficients; in addition, the austenitic is not stable enough, and some Aussene can be transformed into martensite under the action of cutting stress; It is easy to decompose and disperse under action, resulting in sclerosis during the cutting process. The phenomenon of processing sclerosis caused by the previous feed or the previous process seriously affects the smooth progress of the follow -up process.
Large cutting force: Stainless steel has a large plastic deformation during the cutting process, resulting in increasing cutting force. Stainless steel has severe processing hardening and high thermal intensity, which further increases the cutting resistance, and it is difficult to curl and break the crumbs.
High cutting temperature: During cutting, the plastic deformation is large, rubbing large with the knife, and large cutting heat; a large amount of cutting thermal heat is concentrated in the cutting area and the knife-dandruff contact interface, and the heat dissipation conditions are poor.