Most titanium alloy thermal conductivity is very low, only 1/7 of steel, 1/16 of aluminum. Therefore, the thermal energy formed in the process of cutting titanium alloys is not easy to quickly transfer to the workpiece or is cut, and the temperature caused by gathered in the cutting area can reach 1000 ° C, so that the knife mouth of the knife is quickly worn, broken, and cracking and cracking. Converted into dandruff tumors, precision hardware processing quickly worn the blade mouth, and caused a large amount of heat for the cutting area to further reduce the service life of the tool.
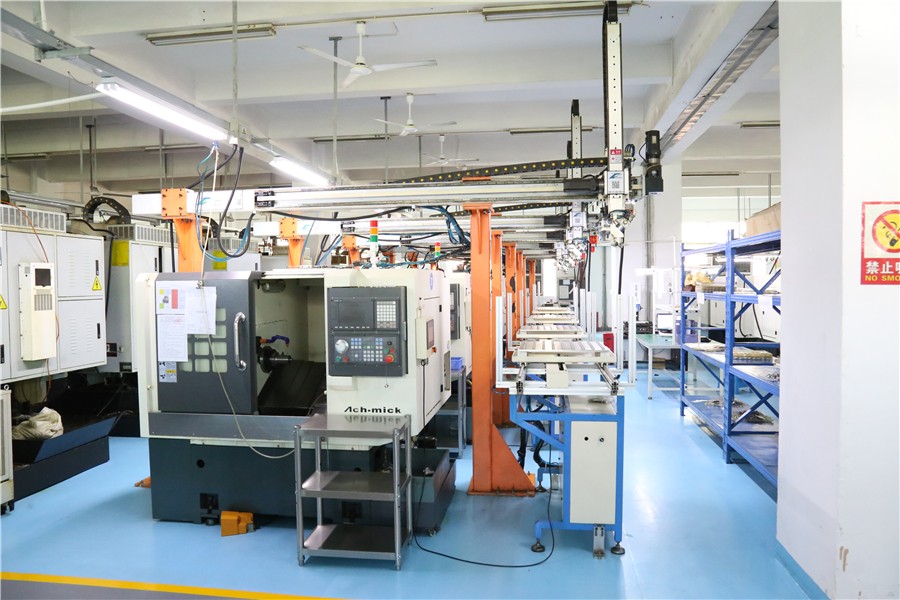

The high temperature formed during the cutting process affects the surface consistency of the titanium alloy parts at the same time, causing a little precision of parts to reduce the cold and hardening status that cannot be optimistic to reduce its fatigue limit.
The elasticity of titanium alloys may be beneficial to parts characteristics, but during the cutting process, the elastic deformation of the hardware processing equipment workpiece is the key cause of vibration. The cutting work pressure of the hardware processing factory leaves the "ductility" workpiece to leave the tool and rebound, and then the friction status of the tool and the middle of the workpiece exceeds the cutting effect. The friction process will also occur, which exacerbates the poor heat transfer of titanium alloy.
When producing and processing thick walls or ring -shaped parts, this problem is even more optimistic. It is not easy to process the titanium -alloy thick wall parts to the expected shape size precision. Because when the workpiece material is pulled open by the tool, the shape monetization of the thick wall has exceeded the category of ductility and forms a plastic variable. At this time, production and processing at the original clear cutting rate are increasing, which further causes the tools to wear sharply. The cutting head tube ditch that often appears during the production and processing of titanium alloys is part of the part of the back and the front of the cutting deep position. It is usually caused by the hard bottoming layer left by early production and processing.